Description
- These step-by-step instructions will guide you through creating, refining and rendering a mesh of one-dimensional linear Lagrange elements.
- The nodal coordinates and element connectivities are read from simple Excel spreadsheets.
-
An automated script that runs this tutorial is included in the Continuity installation: examples\mesh10\1d_example.py. To run it, click File→Scripts→Read script→Python or session script
Start Continuity
- Launch the Continuity Client
-
On the About Continuity startup screen
-
leave the mesh checkbox checked under Use Modules:
-
-
Click OK to bring up the main window
Create initial mesh
-
-
Select rectangular cartesian in the Global Coordinates: pop-up menu
-
Click OK to submit Coordinate Form
-
-
-
Choose Lagrange Basis Function→1D→Linear
-
Click Add Linear
-
Choose Hermite Basis Function→1D→Cubic
-
Click Add Cubic
- Verify that the list of basis functions now contains:
- Linear Lagrange 3
- Cubic Hermite 3
-
Click OK to submit Basis Form
-
-
-
Click Import/Export/Graph button to open Continuity Table Manager
-
Continuity Table Manager→File→Open…
-
Select tab-delimited nodes file (nodes.xls)
-
-
- You should now have nodes numbered 1-2
-
Click OK to submit Node Form
-
-
-
Click Import/Export/Graph button to open Continuity Table Manager
-
Continuity Table Manager→File→Open…
-
Select tab-delimited elements file (elems.xls)
-
-
- You should now have only one element in the list
-
Click OK to submit Element Form
-
-
-
If the Dimensions Form appears, simply click Apply Marked Recommendations and then OK
-
-
-
Click OK to submit
-
Calculate nodal derivatives with respect to local coordinates
-
-
Enter 1 for the xi1, xi2, and xi3 fields under New Element per old element in
-
Select the Local coordinates radio button under New nodal derivatives with respect to:
-
Click OK to submit
-
-
- Verify that you still have only 2 nodes
-
Select Cubic Hermite 3 under Coordinate 1, Coordinate 2, and Coordinate 3
-
Click OK to submit Node Form
-
-
Enter LocalDerivs.cont6 next to File Name:
-
-
-
If the Dimensions Form appears, simply click Apply Marked Recommendations and then OK
-
-
-
Click OK to submit
-
- Return to the Nodes Form and note that derivatives wrt xi(1) are no longer zero
Convert to nodal derivatives with respect to arc length coordinates
-
-
Enter 1 for the xi1, xi2, and xi3 fields under New Element per old element in
-
Select the Arc lengths radio button under New nodal derivatives with respect to:
-
Click OK to submit
-
-
- Verify that you still have only 2 nodes
-
Verify that the derivatives are now 0.8 and 0.6
Render the mesh
-
-
Leave the Open Mesh, Client, and Server checkboxes checked
-
Click OK
-
-
-
Locate and select the LocalDerivs.cont6 saved earlier (or whatever you named it)
-
Click Open
-
-
-
Click the lines radio button
-
Click Render to display mesh
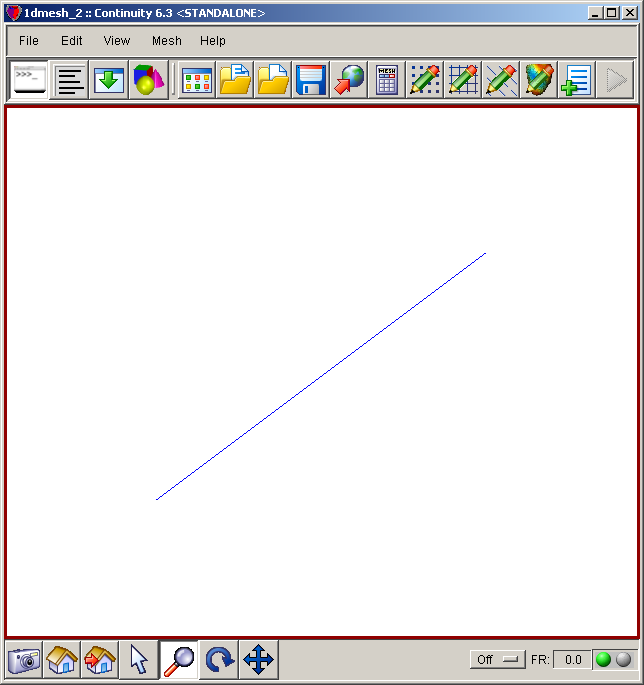
- The mesh should now look similar to the first screenshot above.
-
-
-
Click on Node 1 under Node List
-
Change wrt s(1) to 0.0 under Coordinate 1
-
Click on Node 2 under Node List
-
Change wrt s(1) to 0.0 under Coordinate 2
-
-
Click OK to submit Node Form
-
-
Click the lines radio button
-
Click Render to display mesh
-
Refine the mesh four-fold and re-render
-
-
Enter 4 for xi1, 1 for xi2, and 1 for xi3 under New Element per old element in
-
Select the Local coordinates radio button under New nodal derivatives with respect to:
-
Click OK to submit
-
-
-
Click the lines radio button
-
Click Render to display mesh
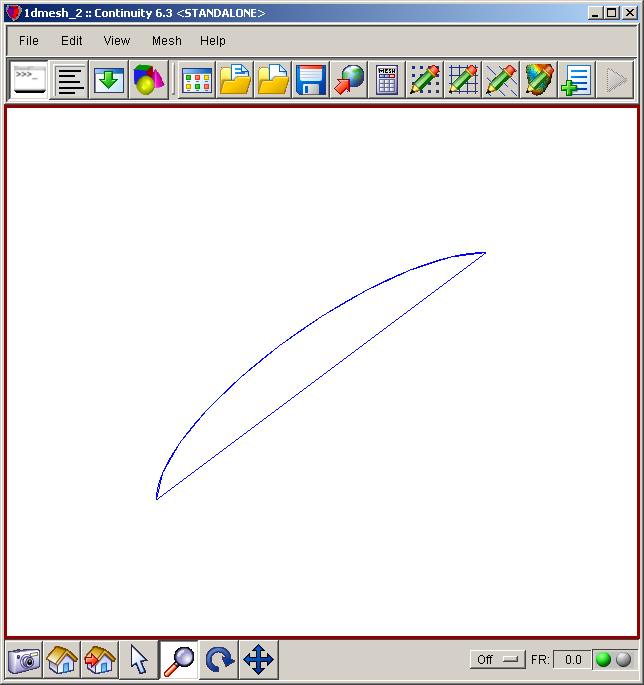
- The mesh should now look like the second screenshot
-
Pre-built model
This cont6 file contains all data and parameters for this problem: mesh2.cont6